8 Top Core AI Agent Components
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and AI Agents
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is rapidly emerging as an essential approach to enhancing visibility and relevance within AI-driven search environments powered by large language models (LLMs). These intelligent search platforms, such as SearchGPT, Perplexity, or AI Overview engines, require a nuanced understanding of their underlying AI agents’ operations. At the core of these agents are distinct components, each playing a vital role in processing user queries, generating meaningful content, and optimizing results to satisfy user intent best.
Understanding these components can empower strategic content creation, optimization, and improved discoverability across increasingly sophisticated AI-powered search tools. Leveraging the insights about each component’s function and purpose provides the foundation for crafting high-quality, authoritative, and contextually aligned content that effectively resonates within AI-based search ecosystems.
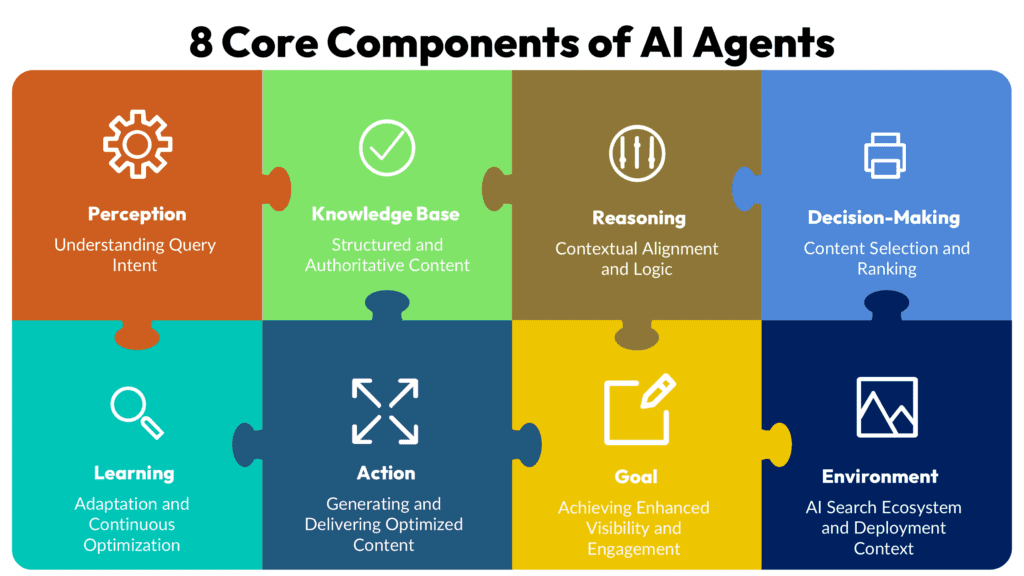
Perception: Understanding Query Intent
Perception refers to the AI agent’s ability to interpret and contextualize user queries accurately. It involves breaking down prompts, determining intent, and identifying underlying user needs. Without precise perception, generative results can misalign with user expectations or queries.
Effective perception enhances the alignment between what users ask and what they receive. The more precise the understanding of a user’s intent, the more accurately content can be generated or retrieved, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement. AI-driven search engines rely on advanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques to dissect and analyze queries in real-time. These processes involve tokenization, intent detection, and semantic mapping to represent what a user seeks.
Perception extends beyond simple keyword matching; it involves understanding nuances, user behavior patterns, and contextual cues. AI search systems can infer intent based on previous interactions, regional influences, or phrasing style. As generative search continues to evolve, refining perception accuracy ensures more personalized, practical, and useful responses.
Examples of use:
- Recognizing the difference between transactional (buying) and informational (learning) queries.
- Identifying implied questions behind ambiguous search phrases.
- Accurately interpreting multi-part queries for comprehensive responses.
- Understanding the conversational context in follow-up queries.
- Detecting subtle language cues that indicate urgency or preference.
Knowledge Base: Structured and Authoritative Content
The knowledge base is a critical repository of structured, authoritative data the AI draws upon when generating responses. It comprises curated, factual, and contextually organized content, serving as the foundation for generating generative results.
A robust knowledge base ensures reliability and credibility in generated content. When content is structured clearly, AI agents can readily access and synthesize this information, enhancing the generative outputs’ accuracy, consistency, and trustworthiness. High-quality, well-organized content reduces the likelihood of misinformation or hallucinated responses, issues that have posed challenges in generative AI search results.
The depth and breadth of a knowledge base significantly impact the quality of AI-generated responses. The more diverse and authoritative the data sources, the better the AI can generate precise, comprehensive answers. Structured data formats such as tables, schema markup, and bullet-pointed content help AI models quickly extract key information. Additionally, a well-maintained knowledge base must be continuously updated to reflect industry trends, regulations, and user concerns.
Examples of use:
- Utilizing structured FAQ sections to answer common questions directly.
- Creating well-defined schema markup for improved AI comprehension.
- Providing comprehensive, authoritative articles and data tables for reference.
- Maintaining regularly updated industry-specific whitepapers and reports.
- Using linked data structures to provide deeper context and relational insights.

Reasoning: Contextual Alignment and Logic
Reasoning involves the AI agent’s capability to logically connect information and contextually align the generated content with the original query. It’s the cognitive layer where semantic and contextual accuracy is established, significantly influencing the quality of the final content.
Practical reasoning leads to meaningful, contextually appropriate, and logically coherent answers. It bridges the gap between raw information in the knowledge base and relevant user-centric results, maintaining logical consistency and semantic precision. Unlike simple keyword matching, reasoning requires AI models to understand relationships between concepts, enabling them to generate informative, well-structured, and logically sound responses.
Reasoning also ensures that generative AI remains adaptable across various query types. Whether answering direct factual questions, responding to complex multi-part inquiries, or providing actionable insights, the AI must process multiple data points while maintaining logical coherence. In AI-driven search engines, reasoning allows LLMs to infer missing details, compare conflicting information, and generate conclusions that align with a user’s search intent.
Examples of use:
- Connecting disparate data points to offer holistic solutions.
- Generating step-by-step explanations to complex queries.
- Aligning content tone and depth to match query sophistication.
- Resolving contradictions in retrieved information by ranking sources.
- Offering nuanced answers by weighing context from multiple knowledge sources.
Decision-Making: Content Selection and Ranking
Decision-making encompasses AI agents selecting, prioritizing, and ranking generated content to best match the original query. It evaluates relevance, quality, and user intent to deliver optimal content results. This process ensures that only the most valuable and contextually appropriate information surfaces, reducing information overload and maximizing efficiency in AI-powered search results.
Strategic decision-making is essential in determining the hierarchy of responses. AI models assess multiple factors, such as engagement history, content freshness, credibility of sources, and alignment with query specificity. By continuously refining these ranking mechanisms, search engines powered by LLMs deliver results that are not only relevant but also actionable. The AI filters out redundant, outdated, or lower-quality outputs to enhance user experience.
Personalization models that analyze user behavior over time influence AI-driven decision-making. Search platforms leverage historical interactions to refine results further, ensuring that users consistently receive the most useful, preferred, and high-engagement content. An effective SEO strategy must consider how AI dynamically ranks content based on user intent and evolving data trends.
Examples of use:
- Prioritizing concise summaries for quick-reference queries.
- Highlighting authoritative sources for credibility-centric searches.
- Filtering and ranking multiple generative outputs based on quality indicators.
- Adjusting content rankings dynamically based on real-time engagement.
- Predicting search trends and preemptively adjusting content visibility.

Learning: Adaptation and Continuous Optimization
Learning represents the adaptive capability of the AI agent to refine responses through continuous optimization based on user feedback, interaction patterns, and evolving data. This component ensures that generative content remains relevant, accurate, and closely tailored to user expectations over time.
Continuous learning allows generative models to evolve, self-correct, and adapt content strategies dynamically. This iterative process gradually enhances performance metrics and user experience. AI-powered search engines rely on machine learning techniques such as reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to adjust content delivery mechanisms based on how users interact with generated results. By analyzing dwell time, click-through rates, and feedback signals, AI models learn to prioritize and refine their outputs for better alignment with user intent.
Additionally, continuous optimization ensures that AI-generated content stays relevant amid shifting industry trends, regulatory changes, and evolving audience expectations. The system enhances its predictive accuracy with each new data point, improving the ability to generate highly relevant and engaging responses.
Examples of use:
- Updating response strategies based on engagement analytics.
- Fine-tuning content recommendations from user preferences.
- Adapting generative language styles to emerging trends.
- Refining topic coverage based on seasonal interest patterns.
- Enhancing AI’s response accuracy through human-in-the-loop training mechanisms.
Action: Generating and Delivering Optimized Content
Action involves the actual creation and delivery of content generated by AI agents. It is the tangible execution of insights gained through perception, reasoning, learning, and decision-making, culminating in a valuable user-facing outcome. AI-powered search engines focus on producing high-quality, digestible, and structured content that meets search engine requirements for readability and clarity.
High-impact action relies on well-optimized content formats, such as structured snippets, detailed explanations, and multimedia enhancements. AI-generated content must be easy to parse, engaging, and tailored to user preferences. Furthermore, ensuring content is formatted with proper headings, lists, and metadata increases its likelihood of being surfaced prominently in AI-powered search results.
Another key element of the action component is multi-format adaptability. LLM-driven platforms increasingly prioritize content suitable for multiple modalities: text, voice search, video captions, and interactive experiences. Optimizing for this range ensures a broader reach and higher discoverability across different user intent scenarios.
Examples of use:
- Crafting concise, informative summaries appearing prominently in AI-generated results.
- Producing structured content snippets optimized for featured placements.
- Creating interactive generative tools such as calculators or decision aids.
- Ensuring AI-generated content is optimized for voice search and conversational queries.
- Implementing structured data to enable content enhancement in AI search results.

Goal: Achieving Enhanced Visibility and Engagement
The goal represents the overarching strategic objective guiding generative optimization, particularly improved visibility, discoverability, and user engagement within LLM-driven search platforms. Clearly defined goals help direct every other component toward generating optimal results.
Explicit goals ensure alignment and consistent outcomes, keeping generative efforts targeted, purposeful, and results-driven. AI-driven search optimization is not just about ranking high—it is about maximizing content engagement, ensuring sustained audience retention, and fostering trust and authority within niche industries. Businesses can maintain high search visibility by refining content based on AI’s evolving ranking criteria.
Moreover, search engine LLMs increasingly prioritize user satisfaction metrics. The more an AI system perceives content as engaging, accurate, and trustworthy, the higher it ranks in search overviews. SEO efforts must extend beyond keyword density and focus on content depth, interactive engagement, and alignment with AI-generated response structures.
Examples of use:
- Increasing content appearances in AI-powered featured snippets.
- Improving engagement through highly relevant generative responses.
- Optimizing content explicitly for higher visibility within AI-generated overviews.
- Aligning AI-generated content with the tone and depth required for industry authority.
- Utilizing AI-specific formatting techniques, such as summarization-friendly structures.
Environment: AI Search Ecosystem and Deployment Context
The environment component encapsulates the platforms, tools, and search ecosystems where generative optimization occurs. The dynamic context influences how generative outputs perform, interact, and evolve effectively. AI-powered search is no longer just about traditional algorithms but about integrating with conversational AI, multimodal search interfaces, and predictive query models.
The environment defines the interactions between content, users, and AI algorithms, directly shaping optimization opportunities. Search engines powered by LLMs evaluate how content performs in various digital landscapes, adjusting rankings based on platform-specific engagement. Generative AI strategies must consider keyword optimization and adaptability across search mediums.
Understanding these environmental nuances enables content to be dynamically adjusted based on AI interaction trends. Aligning content with the AI search environment ensures long-term discoverability through structured data, real-time indexing strategies, or voice-search optimization.
Examples of use:
- AI-powered search platforms like SearchGPT, Grok, Andi, or Perplexity.
- Dynamic content ecosystems, influencing real-time ranking signals.
- Interactive AI result interfaces shaping user engagement patterns.
- Optimizing content for both AI-generated overviews and detailed search results.
- Leveraging AI-friendly content formats such as data-driven insights and multimedia enrichment.

Effective Generative Engine Optimization leverages these interconnected components; decision-making, action, goal, and environment; to refine and strategically position content within advanced AI search platforms. Mastery of these elements translates directly into greater visibility, engagement, and performance.
As AI-powered search becomes increasingly sophisticated, understanding the interplay of these components is essential. Structured, authoritative, and contextually relevant content around these principles ensures consistent optimization outcomes.
Ultimately, Generative Engine Optimization provides a foundational roadmap for navigating and succeeding in a content landscape increasingly dominated by large language model technologies. The strategic alignment and continuous refinement across these components define effective, future-ready content optimization in a rapidly evolving AI search landscape.
Ready to Grow Your Search Engine Results?
Let Digital Results assist you in your SEO strategy and help
deliver the search engine results you need.